View Controller Lifecycle
View Controller Lifecycle是什么
即一系列发送至View Controller消息的生命周期
为什么要关心View Controller Lifecycle
通常我们会在项目的子类中腹泻这些发送给View Controller 的消息,来了解我们的应用正在干什么. 我们可能希望做一些决定或其他操作在View Controller 生命周期的某一个特定时刻
View Controller Lifecycle如何工作
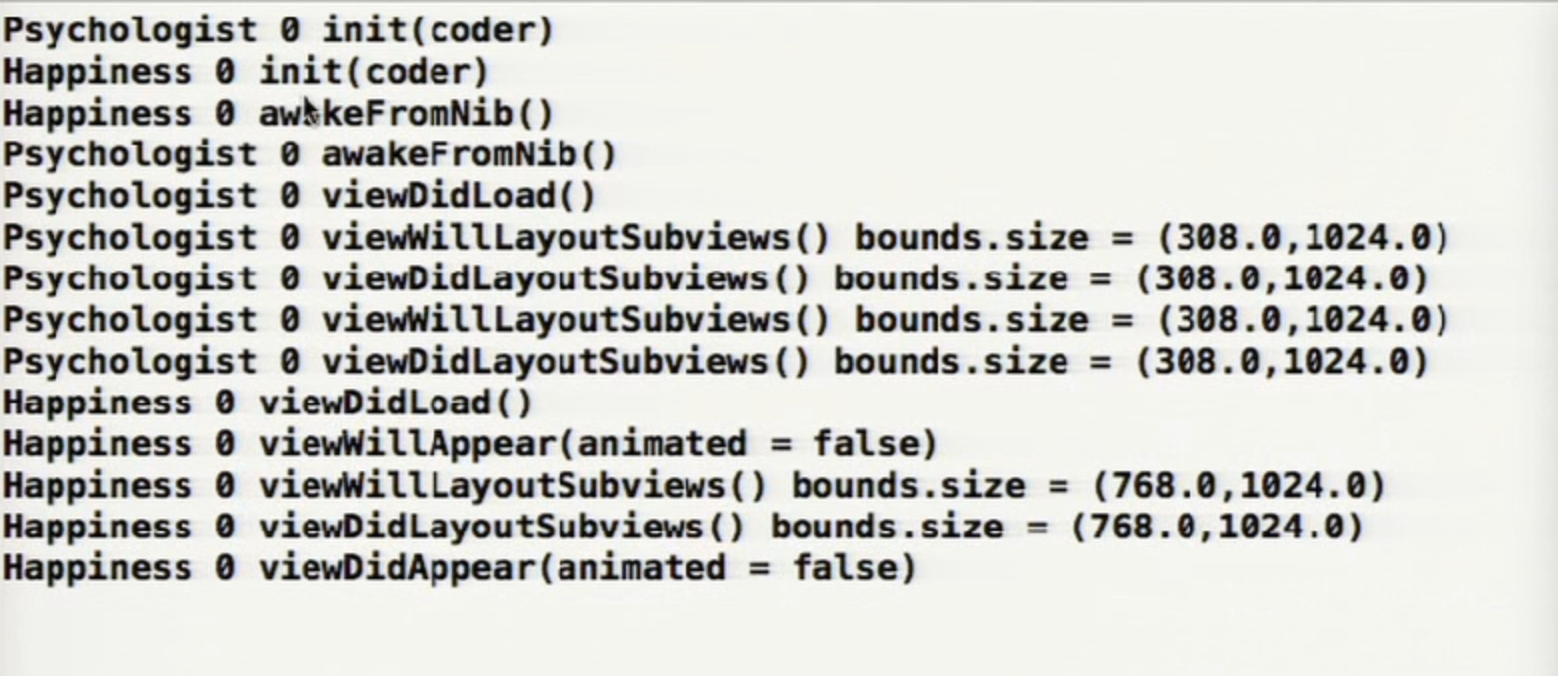
1.从StoryBoard中得到实例化
2.得到awakeFromNib
3.segue准备发生
4.outlets将被系统设置
5.viewDidLoad方法将被调用
6.View将会出现并且消失(viewWillAppear,ViewDidAppear,viewWillDisappear,viewDidDisappear)
7.随着视图控制器的几何变化(屏幕翻转)viewWillLayoutSubview方法被调用,然后是viewDidLayoutSubview.这也许会发生很多次
8.如果可用内存很小,可能会得到内存警报(didReceiveMemoryWarning)
viewDidLoad
在viewDidLoad中初始化视图代码是最好的方式,因为在viewDidLoad进行加载前,segue已经准备完毕、outlets的设定已经完成.不要忘记调用super.viewDidLoad通常我们在viewDidLoad中做的是更新UI,一旦我们的Model发生了改变,我们的Model会在属性观察器中更新UI.所以最好在viewDidLoad中进行UI更新
注意:不要在viewDidLoad中做与几何位置相关的操作.
Autolayout
Autolayout主要是通过StoryBoard来进行实现, Autolayout还是要在自己不断的使用和调试中积累经验,在此不做过多的叙述.
Hugging priority与Compression Resistance priority
Hugging priority 确定view有多大的优先级阻止自己变大。
Compression Resistance priority确定有多大的优先级阻止自己变小。
很抽象,其实content Hugging就是要维持当前view在它的optimal size(intrinsic content size),可以想象成给view添加了一个额外的width constraint,此constraint试图保持view的size不让其变大:
view.width <= optimal size
此constraint的优先级就是通过上面的方法得到和设置的,content Hugging默认为250.
Content Compression Resistance就是要维持当前view在他的optimal size(intrinsic content size),可以想象成给view添加了一个额外的width constraint,此constraint试图保持view的size不让其变小:
view.width >= optimal size
此默认优先级为750.
参考:AutoLayout中的Content Hugging 和 Content Compression Resistance
AutolayoutDemo
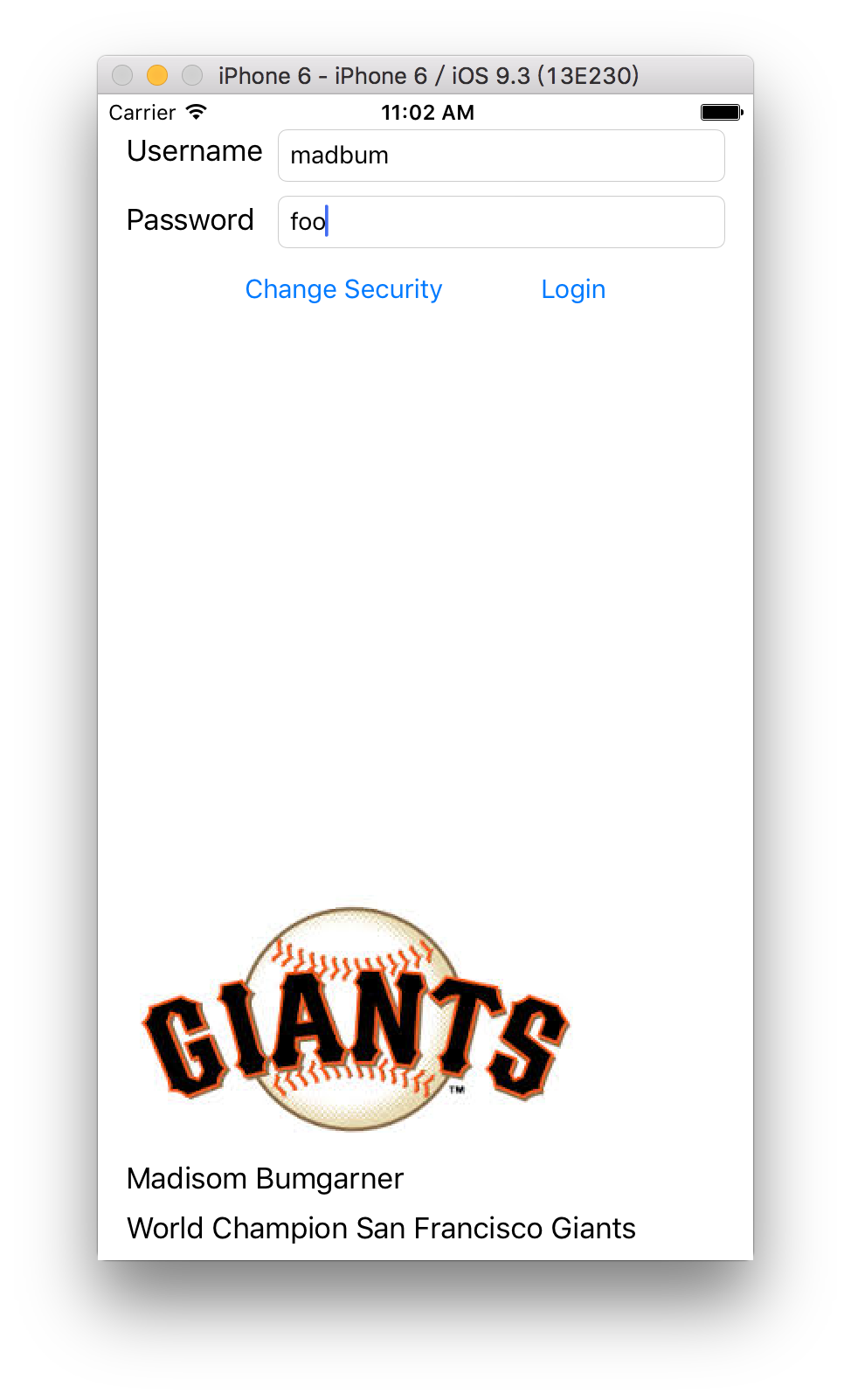
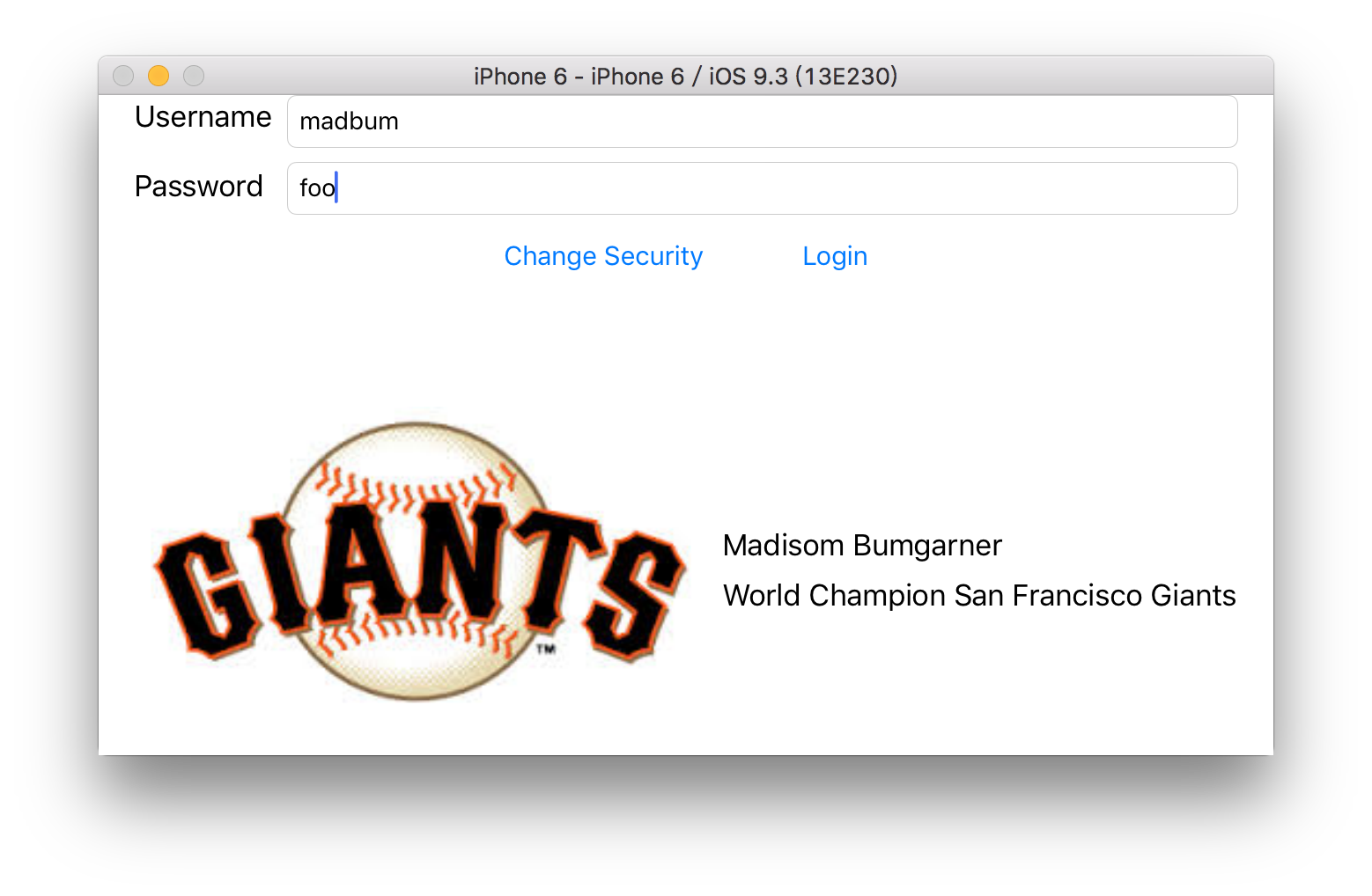
本课跟随教程实现了一个小登录器的项目,主要是调试登录后图片的自动布局及旋转后的布局,大多数布局由StoryBoard上的操作完成,图片的自动布局有代码来完成.DEMO的代码如下
//viewController
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var LogingField: UITextField!
@IBOutlet weak var passwordField: UITextField!
@IBOutlet weak var passwordLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var nameLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var companyLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var imageView: UIImageView!
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
updateUI()
}
var secure = false {
didSet {
updateUI()
}
}
var loggedInUser: User? {
didSet {
updateUI()
}
}
private func updateUI() {
passwordField.secureTextEntry = secure //设置密码框的加密输入,为true时密码被替换为***,为false时直接显示输入值
passwordLabel.text = secure ? "secured Password" : "Password"
nameLabel.text = loggedInUser?.name
companyLabel.text = loggedInUser?.company
image = loggedInUser?.image
}
@IBAction func toggleSecurity(sender: UIButton) { //改变密码显示方式
secure = !secure
}
@IBAction func login() {
loggedInUser = User.login(LogingField.text ?? "", password: passwordField.text ?? "")
}
var image: UIImage? {
get {
return imageView.image
}
set {
imageView.image = newValue
if let constrainedView = imageView {
if let newImage = newValue { //设置约束
aspectRatioConstraint = NSLayoutConstraint(item: constrainedView, attribute: .Width, relatedBy: .Equal, toItem: constrainedView, attribute: .Height, multiplier: newImage.aspectRatio, constant:0)
}else {
aspectRatioConstraint = nil
}
}
}
}
//NSLayoutConstraint为所有约束的class
var aspectRatioConstraint: NSLayoutConstraint? {
willSet { //在未设置前清除已存在的约束
if let existingConstraint = aspectRatioConstraint {
view.removeConstraint(existingConstraint)
}
}
didSet { //设置约束
if let newConstraint = aspectRatioConstraint {
view.addConstraint(newConstraint)
}
}
}
}
//对Model进行扩展,添加image
extension User {
var image: UIImage? {
if let image = UIImage(named: login) {
return image
} else {
return UIImage(named: "unknown_user")
}
}
}
//保证图片宽高比与原图一致
extension UIImage {
var aspectRatio: CGFloat {
return size.height != 0 ? size.width / size.height : 0
}
}
//Model
import Foundation
struct User {
let name: String
let company: String
let login: String
let password: String
static func login(login: String, password: String) -> User? {
if let user = datebase[login] {
if user.password == password {
return user
}
}
return nil
}
//数据库
static let datebase: Dictionary<String, User> = {
var theDatabase = Dictionary<String, User>()
for user in [
User(name: "John Appleseed", company: "Apple", login: "japple", password: "foo"),
User(name: "Madisom Bumgarner", company: "World Champion San Francisco Giants", login: "madbum", password: "foo"),
User(name: "John Hennessy", company: "Stanford", login: "hennessy", password: "foo"),
User(name: "Bad Guy", company: "Criminals Inc", login: "baddie", password: "foo")
] {
theDatabase[user.login] = user
}
return theDatabase
}()
}
参考:Stanford CS193p iOS开发课程笔记(七)
SourceCode:Autolayout